Shapella is Here: How ssv.network Supports the Full ETH Staking Lifecycle
Discover Ethereum's Shapella update, enhancing the staking ecosystem with secure ETH withdrawals and boosting flexibility for stakeholders across the network.

It’s official! The ETH staking lifecycle is up and running. Shapella might not have been the “biggest” update to Ethereum. But it has been crucial for the staking industry and every stakeholder therein.
Shappella gets its name by combining two of the latest upgrades (the Shanghai Upgrade and the Capella Upgrade). This naming convention signifies the first simultaneous upgrade of Ethereum’s EL (execution layer) and CL (consensus layer).
With the aim of Distributed Validator Technology (DVT) becoming Layer 0 for Ethereum, withdrawals have been a shared milestone for ssv.network on the road to our mainnet. So,
If you’re wondering, keep on reading…
Now that the merge has passed and withdrawals have been enabled through Shapella, the full ETH staking lifecycle is officially finalized. After more than two years, stakers can withdraw their accumulated rewards or even fully exit the Beacon Chain. All eyes are on Ethereum and its validators.
What is Shapella? Shapella is more than just withdrawals. This update brings a variety of improvements to the Ethereum blockchain. These advancements have far-reaching effects on the network as a whole.
Improved Security:
Changes to the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) reduce the impact of potential attacks.
Smart contract upgrades:
The update will include improvements to the smart contract language and tooling. Better smart contracts make it easier for developers to build and deploy smart contracts on the Ethereum network.
Improved security and efficiency of smart contracts. This is done by limiting the amount of gas that can be used during the contract initialization process. Limiting the amount of gas that can be used also provides more accurate gas metering.
Withdrawal of staked ETH:
The update will introduce the ability to withdraw staked ETH, giving users more flexibility and control over their funds.
Overall, Shapella has brought significant upgrades to the Ethereum network. This could, in turn, drive innovation in the staking industry and open up new opportunities for stakers and developers alike.
On to the juicy stuff. What do withdrawals and unlocked liquidity mean for validators and the staking ecosystem as a whole?
Now that the staking process is finalized from beginning to end, Ethereum staking has been validated.
Many, including Consensys, surmise that withdrawals will lead to new stakers and validators joining the ecosystem. Expect to see more institutions, services, and solo stakers entering the space.
The effects of withdrawals on stakers & the staking ecosystem:
A Liquid ETH Supply:
The ability to withdraw staked funds gives users more flexibility to manage their ETH. This also means that Liquid Staking Tokens (LSTs) are no longer the only way to make staked ETH liquid.
Users can choose to withdraw their rewards or capital at any time. This can be particularly useful in cases where stakers want to participate in DeFi.
Increased competition:
The ability to withdraw staked funds could also increase competition in the staking industry. If users are not locked into a staking contract, they can move their funds to different staking opportunities as they arise.
More liquidity in the market means it becomes easier for developers to create complex staking products tailored to different users’ needs.
Innovation in staking models:
The increased efficiency and accessibility of staking on the Ethereum network could also lead to innovation in staking models and new ways of using staked ETH.
For example, we could see the development of new DeFi applications that use staked ETH as collateral or offer new forms of rewards for staking.
Liquid Staking Infrastructure:
Out of the almost 18 million ETH staked, liquid staking makes up the majority (8.1 million) of the staking ecosystem. A more liquid ETH supply can drive demand for solutions, improve staking liquidity, spur the development of more sophisticated products, and increase competition among providers.
For more information on withdrawals and how to participate, check out the official documentation.
Since the genesis of Ethereum’s PoS transition, Distributed Validator Technology (DVT) has been developing in parallel.
Withdrawals create an opportunity for innovation as well as DVT to shine. The ssv.network is perfectly positioned to support developers, service providers, and stakers in this new era.
With 18 million staked ETH unlocked, there is potential for a massive liquidity reshuffle. Once liquid, ETH can be delegated to different services, i.e., Liquid staking protocols or DeFi. Or both!
In the staking ecosystem, a risk curve exists for stakers. The higher the yield, the more risk users expose themselves to. Going up each level in the risk curve is essentially using an additional technology stack. Inadvertently increasing the risk to the user.
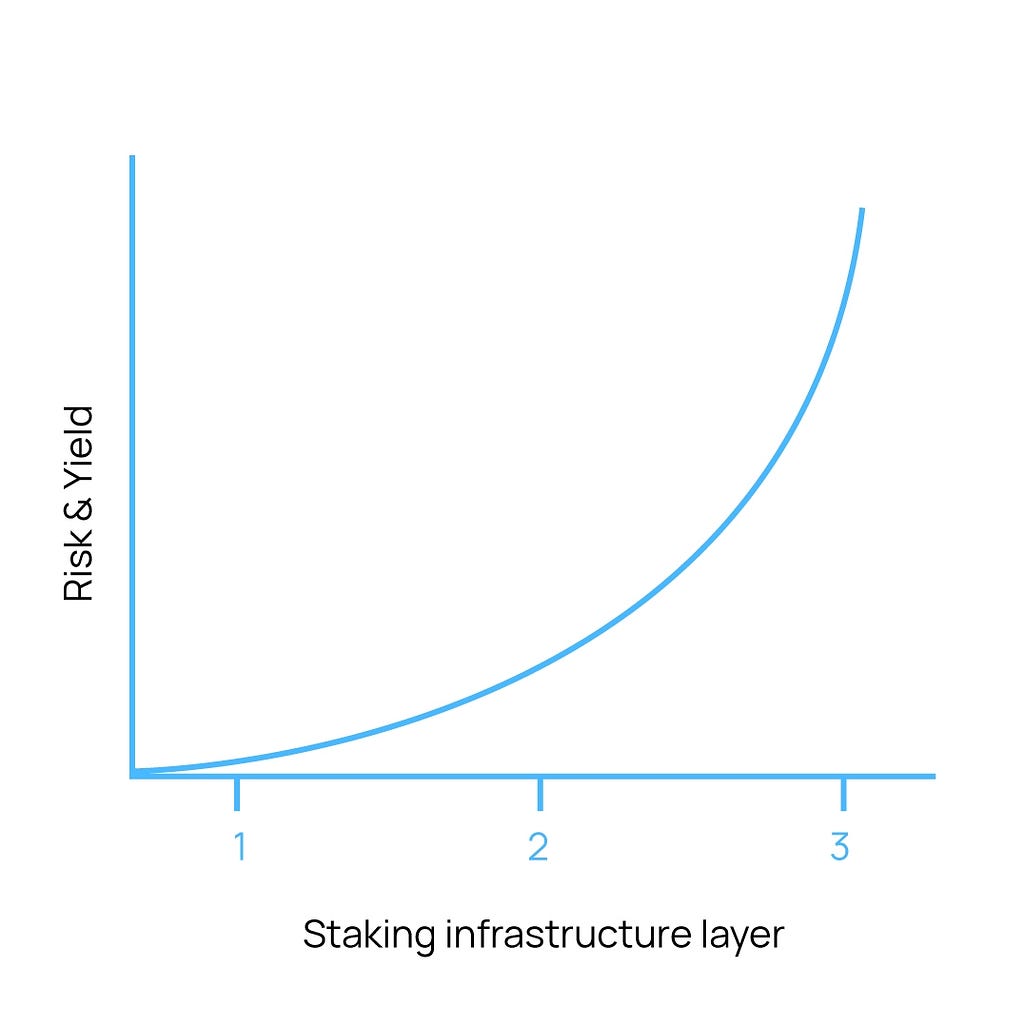
For example, staking directly on the Beacon Chain. This is one complex layer of infrastructure. But it’s only one layer. When using a protocol like Lido or Stakewise, users are exposed to more risk. Two layers, both the Beacon Chain and that of the service provider.
Now add in a protocol like AAVE, and you have three layers. Your yields are much higher than just staking directly on the Beacon Chain, but you’ve exposed yourself to much more risk. And just like stakers, service providers also have risks when they rely on various node operators or when they have to create infrastructure themselves.
Validator infrastructure can be complex and take up a lot of time to get it right. The ssv.network can minimize these challenges by allowing stakers, builders, and service providers to employ our ready-to-use decentralized validator infrastructure.
To help support this major transition, DVT can play a critical role in bolstering staking infrastructure and improving the staking process’s overall resilience and user experience.
How ssv.network helps de-risk the staking ecosystem:
Solo-stakers
Instead of running their own validator infrastructure, solo-stakers can register their validator key on the network and benefit from the fault tolerance of a decentralized validator. DVT allows stakers to optimize their staking APR by improving uptime and reducing slashing risk.
Developers
Easy-to-use infrastructure speeds up the building process for builders. Having an infrastructure layer for validators that’s ready to go means developers can focus on their product and less on infrastructure complexities. There are numerous use cases for ssv.network custom smart contracts.
Service providers
Everything is becoming modularized. Use the ssv.network to mitigate infrastructure risk. Instead of requiring an entire team and the associated costs and complexity of developing infrastructure, service providers can use a network of nodes to manage their validators in a distributed manner.
Stake Centralization
While centralized entities have made staking more accessible for non-technical users, most of the ETH stake still sits with a handful of service providers. Entities like centralized exchanges can use DVT to distribute their own infrastructure. DVT can help diversify Ethereum’s validation layer throughout the entire stack.
Ethereum’s Shapella update brings various improvements, including the ability to withdraw staked ETH. It provides users with increased flexibility and reduced risk of having funds locked. Withdrawals also open up new opportunities for innovation in the staking industry and new ways of using staked ETH. The next step is to make participating in staking as user-friendly and safe as possible. DVT will play a crucial role in this transition and ssv.network is here to help.
Enabling withdrawals has provided a unique opportunity for innovation and growth. While we continue to test our mainnet candidate, Jato, we are gearing up to go live! Take part in our final test and see what the future of staking looks like.
Website | Network Hub | Discord | Dev Center | Documentation | GitHub