SSV Builders: StakeWise
Integrating DVT into StakeWise V3 improves staking by decentralizing validators it allows for permissionless node operation & liquid staking.

Decentralizing Ethereum and opening it up for all kinds of stakers — while maintaining overall network health — has become a significant focus point for the ecosystem. Because Staking as a Service (SaaS) can reduce the 32ETH capital requirement, help overcome the technical barriers of running infrastructure, and supply additional benefits like Liquid Staking Derivative (LSDs), the majority of stakers have flocked to SaaS providers. Leading to a hand full of services holding the majority of staked ETH.
This leaves the ball in the SaaS provider’s side of the court. Essentially, they have the choice to continue as is or implement new solutions that create a win-win for the ecosystem. StakeWise is a good example, and one of the solutions that help them achieve their goal of “maximizing the health of the Ethereum ecosystem” is Distributed Validator Technology (DVT).
At its core, DVT aims to decentralize Ethereum validators by splitting the validator key into KeyShares. These KeyShares are distributed to multiple operator nodes that handle the duties of the validator by recreating the full validator key with each of their individual shares when they are needed. This means that a validator can be operated by multiple nodes, each with its own client(s), hardware, and location — a major bonus for network health and diversity.
By integrating DVT into the upcoming Stakewise V3 upgrade, the team can enable permissionless node operation and liquid staking that’s resilient to slashing. Allowing the system to be flexible enough to accommodate the needs of all sorts of users while simultaneously supporting the Beacon Chain at scale.
First of all, let’s look at solo-stakers, a class of staker seemingly undercut by all the recent developments within the staking industry.
Integrating DVT into StakeWise V3 has helped turn the protocol into a new type of beast from its previous version. StakeWise V2 implemented the stand-alone Stakewise pool, where the StakeWise DAO approved the operators on behalf of its stakers. With V3, the protocol moves to a fully permissionless system where anyone capable of running a node can run their own staking pool (Vault), creating an open marketplace where stakers select different operators according to their needs. Additionally, V3 introduces a new liquid staking token, osETH, providing all users of StakeWise V3 access to their staked capital.
The flexibility of Vaults, combined with osETH, create unique opportunities, for example:
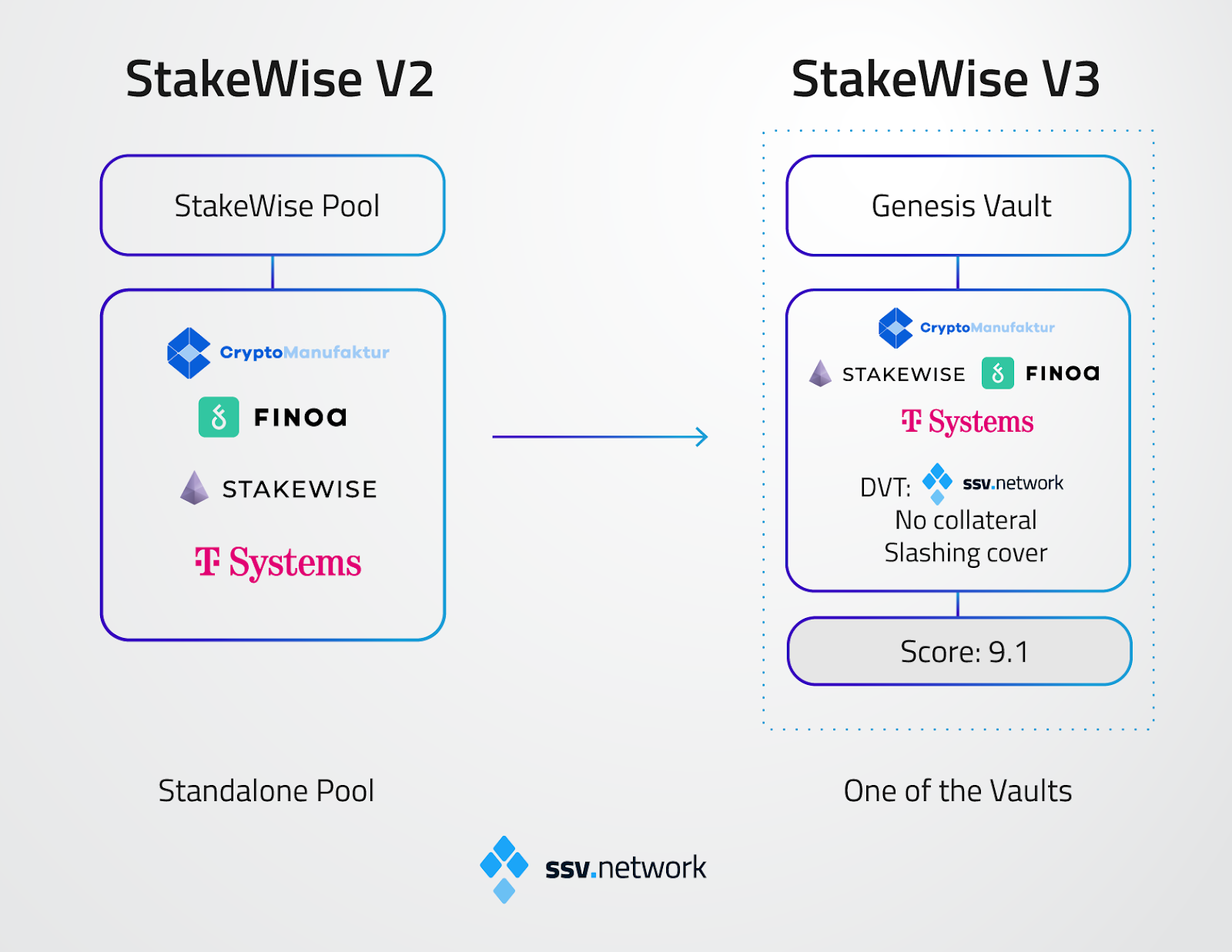
The current Pool will become the first Vault in StakeWise V3, codenamed “Genesis”. Upon transition, it will maintain the same operator set (Cryptomanufaktur, Finoa, StakeWise Labs, T-Systems) and commission (5% of rewards for operators), leaving no impact on how users’ Ether is being staked. However, validators will now be able to move to different vaults with different node operators and value propositions.
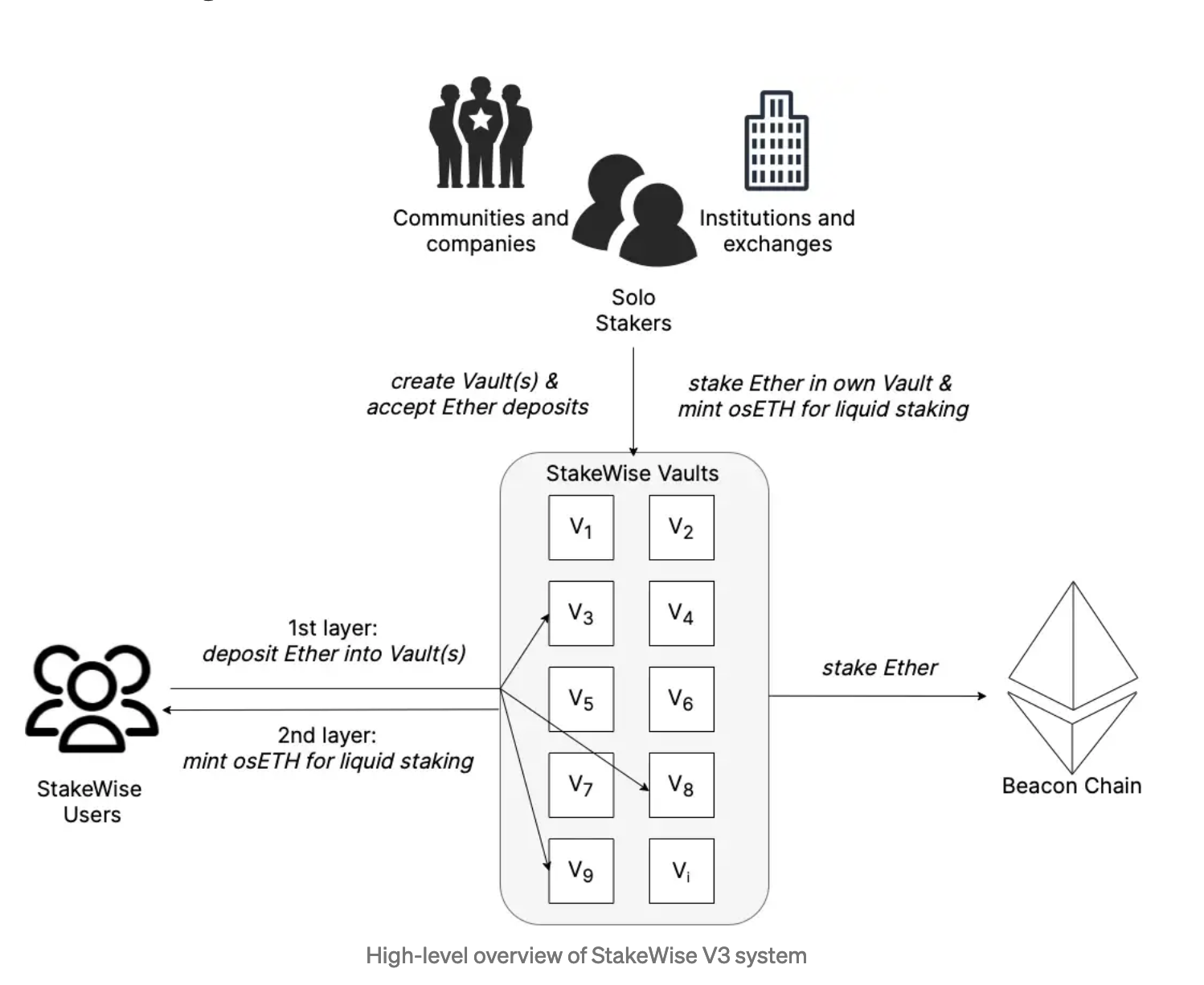
At the heart of the protocol lies a network of Vaults — individual staking “shops” that anyone can set up to accept Ether delegations in return for a staking fee. Vaults can be formed by either a single party running the nodes or multiple parties working together. In some Vaults, DVT (SSV) is used, giving a vast array of operators in each vault the opportunity to hold one of the keyshares. For example, Vaults can be formed by:

When staking, security and uptime have always been the name of the game. To provide more transparency, StakeWise is implementing a new automated scoring system for Vaults, considering vault profitability and operators’ performance in the vault (regardless of who the node is operated by).
The score will include metrics such as:
The weight of parameters are decided by the StakeWise DAO and can be changed by vote. Users will realize that the scores for DVT-enabled vaults are higher than those without them. This is mainly due to the higher degree of fault tolerance (splitting the validator key) and client diversity (having multiple operators with unique setups) that inherently come with DVT.
Now that validators are securing the Ethereum blockchain, we need to look at them as more than just a means of receiving staking rewards. They are the mechanism that secures all the data that we, as the ecosystem, need to continue the things that we do. By simplifying and improving the staking process, StakeWise and other protocols that integrate SSV can effortlessly usher in a new wave of network participants that assure the health of the Ethereum network.
Website | Network Hub | Discord | Dev Center | Documentation | GitHub