Revolutionizing ETH Staking: The Rise of Distributed Validator Technology and SSV.Network
Discover how ssv.network is changing the ETH staking landscape with Distributed Validator Technology (DVT), enhancing security and decentralization.

As we all know by now, Shapella has enabled withdrawals for Ethereum validators. A major milestone that’s finally completed the ETH staking lifecycle.
The question is, what’s next for validators?
TL;DR it’s Distributed Validator Technology (DVT).
In this post, we’re going to look at:
During the genesis of the Ethereum Beacon Chain, when founders were running a validator for the Ethereum 2.0 testnet, they experienced downtime due to a hardware failure. They realized that at scale, a single point of failure could jeopardize the entire network. Prompting them to add a solution early on in the Ethereum Roadmap.
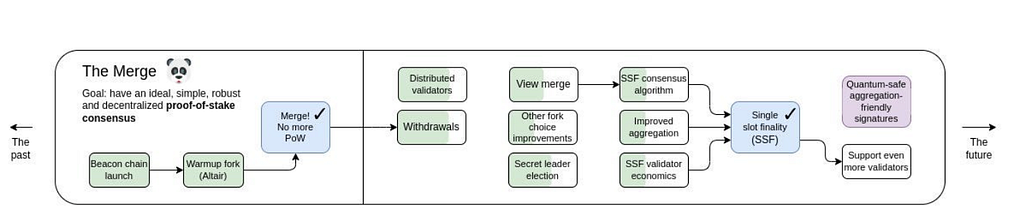
SSV (Secret Shared Validators), later renamed DVT, was a proof-of-concept we created in partnership with the Ethereum Foundation to solve the problem of validator fault tolerance. DVT allows a standard validator to be run by multiple parties in a secure and decentralized manner.
One of the first DVT implementations was the ssv.network. A meshlike network comprised of nodes (a.k.a Operators) that finally provide active-active redundancy to validators. Since then, it has matured into a community-driven project and enterprising ecosystem that aims to improve the security and decentralization of Ethereum. And it’s almost live…
After countless hours of R&D, building a developer ecosystem with a global community, and running public testnets for over two years. The ssv.network is finally ready to be the first DVT Network implementation to go live on the Ethereum mainnet.
According to Vitalik’s Ethereum roadmap, the next crucial step for Ethereum’s validation layer is DVT. It provides a way to distribute validators across 4,7,10, or even 13 nodes, exponentially improving their resilience and decentralization of the network.
The ssv.network was designed as an infrastructure layer — what we call a DVT Network. This makes the protocol a ready-to-use, permissionless, and trustless network of nodes. Locked and loaded to bootstrap onto any staking application, solo operation, or service.
Stakers only need to register their validator key to the network. Choose which nodes they want to manage their validator (based on location, client, or performance). The rest is taken care of by the network. A truly non-custodial staking experience without infrastructure worries.
Developers can use the custom ssv.network smart contracts to create and seamlessly deploy various decentralized staking use cases.
Service providers can bootstrap the network to their current operation and distribute their validator infrastructure. Service providers can also open up their services up to the public. Entities with existing infrastructure can create a new revenue stream by maintaining validators in the network.
Do you want to keep your service private or only serve specific clients?
Become a permission operator, and provide services to white-labeled validators while keeping all the benefits of ssv.network.
Withdrawals have finally unlocked what feels like nearly pre-historic ETH. Since Shapella, there has been a considerable outflow of ETH from the staking contract. A gross total of ~3 million ETH has been withdrawn already.
Making once-staked funds liquid allows stakers to put their stake in more robust and advanced services. Rather than directly staking on the Beacon Chain and locking up funds, users will look for a more convenient way to stake.
Liquid Staking Tokens (LSTs) currently hold the majority of the market share in the ETH staking ecosystem. Due to their use case, the industry is set to grow.
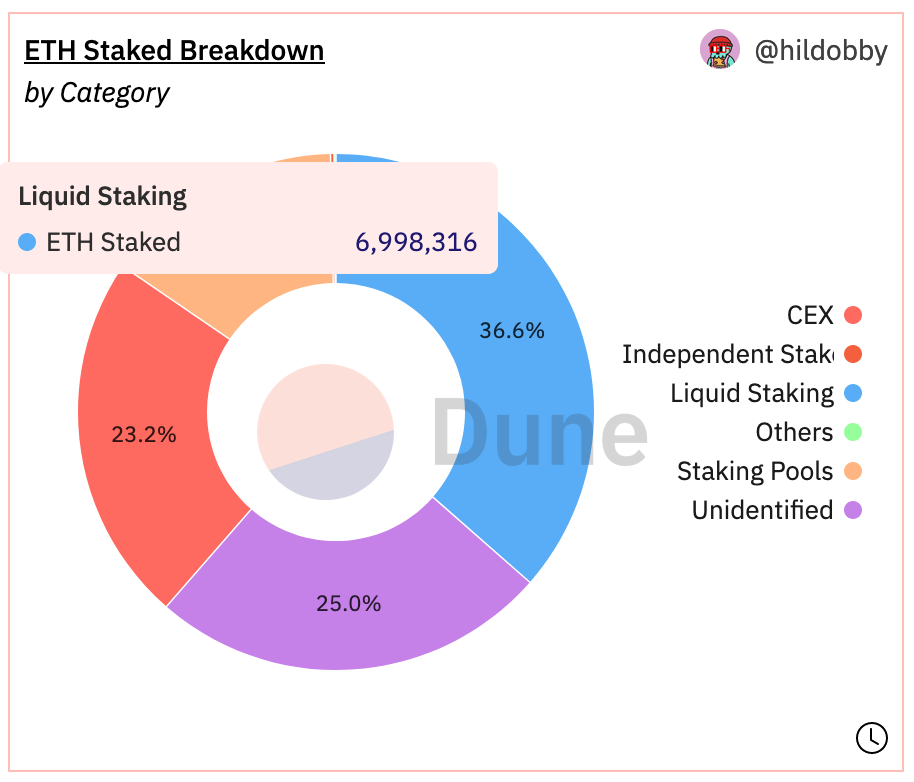
Those who can provide safer, more robust services will have a clear advantage over the competition. These projects stand the best chance to capture the next wave of liquid ETH entering the ecosystem.
As the Ethereum network makes a push toward decentralization, various services are following suit by transitioning into more decentralized designs.
Stakewise, Rocket Pool, and Lido are all examples of liquid staking models that embrace a modular approach. By giving users more choice over how validator nodes are set up.
As we can see, DVT is getting ready for its time in the limelight. Some of the biggest staking projects have already started testing DVT in their services.
The technology plays a central role in the design of various staking projects, facilitating permissionless node operation and liquid staking that is resilient to slashing. The result is a more robust and secure Ethereum and a better user experience for ETH staking.
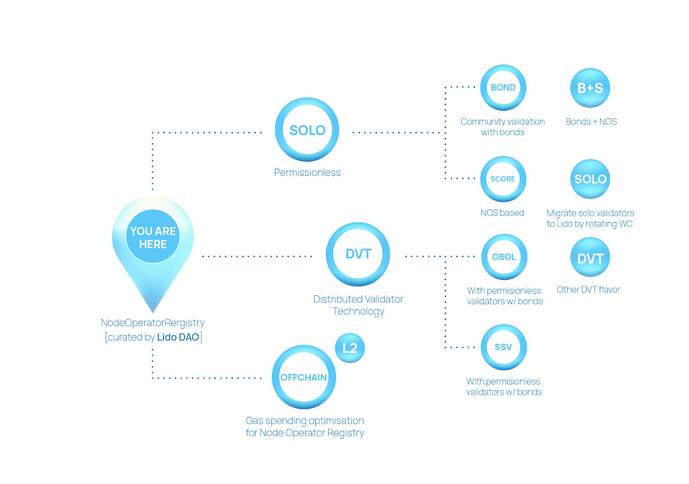
By integrating DVT solutions, Lido V2 will be able to add validators run by a mix of permissioned and permissionless actors. A major win for decentralization. Moreover, it can reduce relevant operator risks for validators created by the Lido permissioned Node Operator set.
Stakewise V3 is implementing DVT in a new staking vault. By utilizing DVT, the system can distribute the validation workload among multiple nodes, minimizing the risks associated with a single point of failure or manipulation by a single entity.
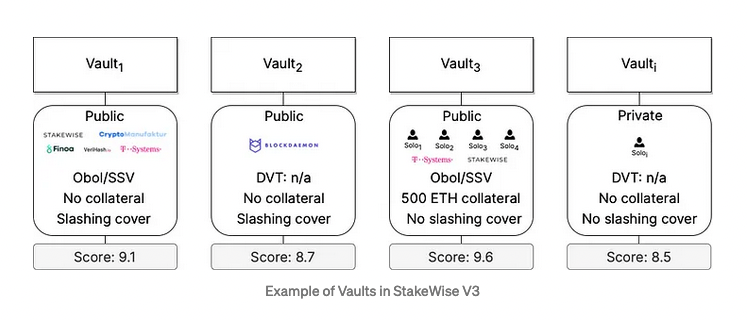
Using DVT enables anyone to run their own nodes without collateral, allowing solo-stakers to allocate ETH to any node operator they prefer. This upgrade turns Stakewise V3 into a fully permissionless system. Where anyone capable of running a node can create their own staking pool. The result is an open marketplace where stakers select different operators according to their needs.
DVT levels the playing field for at-home stakers. For Rocket Pool the implementation of DVT helps address the maintenance and performance concerns that may negatively impact the long-term rewards of solo-stakers.
In some cases, it gives solo stakers a whole new advantage. Once DVT is implemented, capital requirements will be able to decrease below the current 8 ETH requirement. For instance, four distributed nodes could form a DVT cluster within a minipool, each depositing 2 ETH.
Individual home stakers often have lower average uptime compared to institutional stakers. With DVT, solo-stakers can worry less about such issues that may impact their staking operations and instead focus on securing the network and earning rewards.
DVT is the logical progression for ETH validators. As the ssv.network starts gearing up for going live, we expect to see DVT becoming a staple across the staking ecosystem. The ssv.network provides the essential infrastructure for anyone participating in the ETH staking ecosystem.
Join us in our final testnet before the network goes live!
Website | Network Hub | Discord | Dev Center | Documentation | GitHub