SSV Builders: Ankr — ETH 2.0 Liquid Staking
Ankr is building a trustless and non-custodial staking solution using SSV infrastructure for institutional Ethereum 2.0 staking.
Builders in the SSV Ecosystem are pushing the frontiers of staking, building applications that can engage a new wave of stakers and validators to join the Ethereum network. Now that The Merge — the transition from PoW to PoS — has passed and Ethereum validators are securing the blockchain, distributed validator technology (DVT) has been set as one of the new focal points according to Vitalik’s updated Eth roadmap. Because PoS and DVT are emerging technologies, various challenges still need to be addressed, among them, trustlessness, custodianship, and fault tolerance.
This post will provide insight into the liquid staking service Ankr is building using SSV infrastructure. We’ll be covering how an SSV-based validator setup can create staking experiences that are more secure, resilient, and trustless; while solving the challenges that most non-DVT validator setups currently face.
The Ankr team are veterans at building Web3 Infrastructure and have received one of the most significant grants the ssv.network DAO has awarded to date. The team provides streamlined access to a global network of both full- and validator nodes running on 20+ different blockchains. While building infrastructure that significantly simplifies the process of building, operating, and maintaining decentralized applications. This allows the team to build services like Ankr Staking, which streamlines the process of interfacing with PoS chains and receive staking rewards.
Stakers that don’t have the required 32 ETH collateral or the technical knowledge to set up and maintain their own validator infrastructure need to trust an intermediary with their stake. Since the tech is new and options for non-custodial staking pools are limited, the majority of stakers lean towards using staking service providers to overcome these barriers. After operating ETH validators in the space for some time, Ankr realized that DVT is a must to make validators more fault tolerant by splitting the validator key between multiple non-trusting nodes. As we speak, the Ankr team is working to remove intermediary risk and solveing the need for decentralized, trustless, and slashing-resistant staking by integrating SSV.
As part of Ankr’s Ethereum liquid staking strategy, the team is developing an SSV-based liquid staking pool that provides trustless and non-custodial staking. SSV infrastructure will help Ankr adapt to the changing staking ecosystem part of Ethereum’s Merge and the Shanghai upgrades when successfully implemented.
Ankr’s liquid staking solution allows ETH holders to participate in Ethereum 2.0 staking and receive staking rewards without running a node and locking up their ETH. To achieve this, Ankr has introduced the Micropools mechanism, a solution for breaking down the economic barriers for Ethereum 2.0 staking. As the name suggests, Micropools allow users to stake in smaller portions (i.e., multiples of 0.5 ETH) towards a validator and receive a proportional reward based on the staked amount. With the upcoming launch of Ankr’s SSV-based liquid staking service, the asset delegation risk will be significantly decreased by removing single points of failure and delegating stakers’ assets to multiple non-trusting nodes rather than a single validator node.
When using Ankr’s SSV-ETH pool, users can take part in the Micropool and receive rewards based on the percentage of their ETH stake. When staking, users will receive a liquid token (either asETHb or asETHc) generated by the staking pool contract.
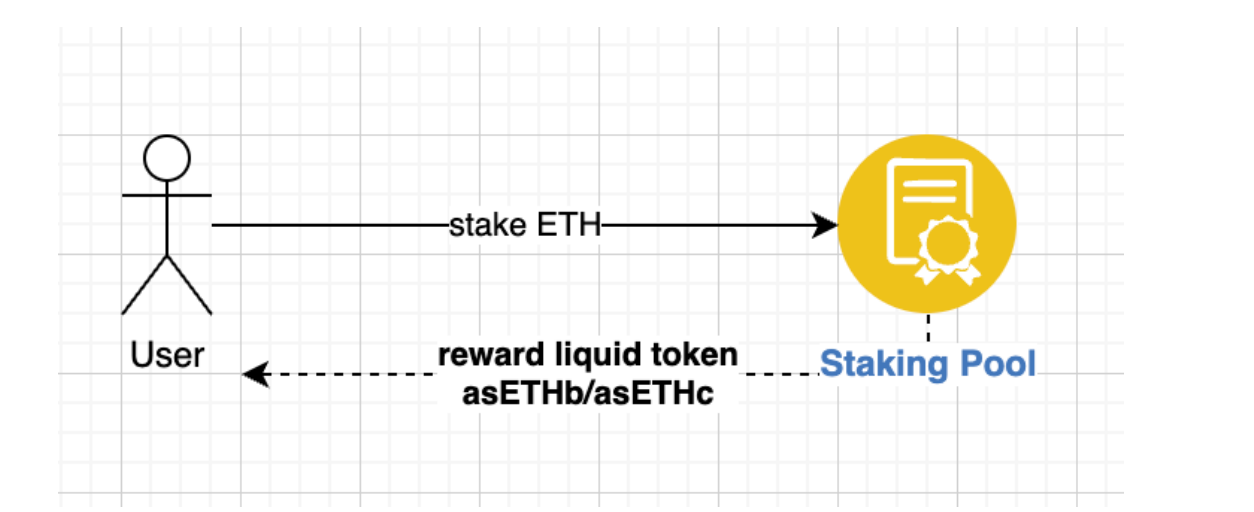
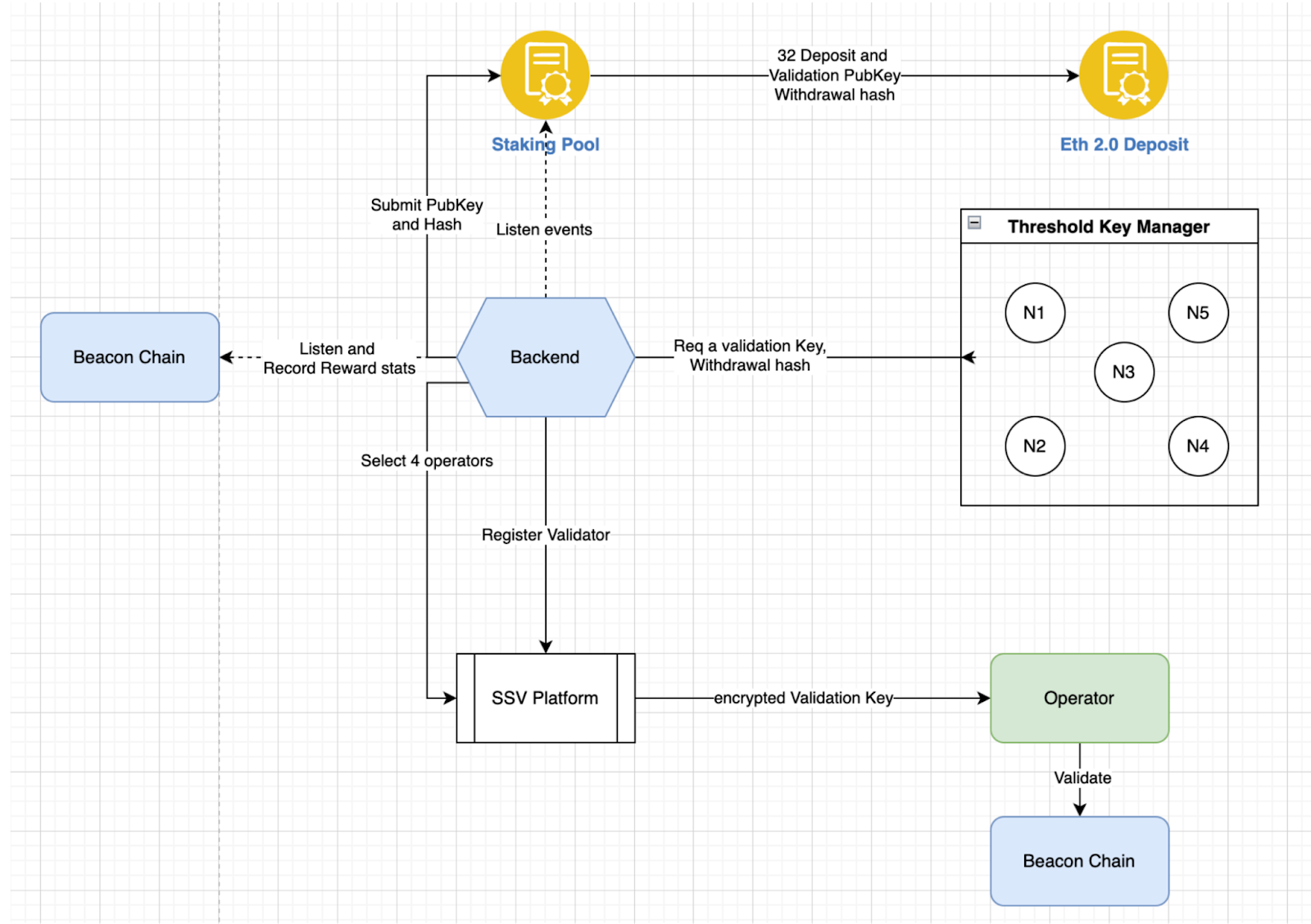
Once the pool reaches 32 ETH, a key pair (validation key, withdrawal key) is generated through the Threshold Key Manager Service, then assigned to SSV nodes, followed by the validator performing duties on the Beacon Chain and helping to decentralize Ethereum. Easy as that!
Liquid Staking Token: asETHb & asETHc
Ankr’s ETH 2.0 staking solution provides a reward mechanism and instant staking liquidity through a new liquid staking token called asETHc.
● asETHc is an asset that represents a user’s ETH stake and receives staking rewards. asETHc does not change in quantity but fluctuates daily to reflect rewards. When a user stakes their ETH, they can redeem asETHc tokens, which can be either kept in self-custody, traded, or used in DeFi products to earn yield.
● asETHb is a rebasing token, and when you hold asETHb, your token balance will increase in proportion to your ETH staking rewards. A rebase runs daily, and the rewards are calculated for each update.
To date, the ssv.network DAO has committed over $1.6 million in development grants to builders expanding the SSV ecosystem. By using SSV infrastructure to build the staking applications of tomorrow, SSV is delivering on its vision to truly decentralize the Ethereum network by making it fully trustless and removing the risk of centralized intermediaries. Have a look at our SSV Builders series to see what our ecosystem is bringing to the staking industry.
Website | Network Hub | Discord | Dev Center | Documentation | GitHub